Dealing with children is fun. But at the same time, it is a difficult task at times. Dental treatments often find children to be uncooperative, panicky and restless while sitting on the dental chair. Anesthesia and dental sedation methods need to be applied to small kids even, in order to carry out the dental procedures smoothly. Kids suffering from dental anxiety are therefore best managed with the help of sedation. You will, therefore, need to hunt for the best sedation dentistry near you to get the dental work done for your child.
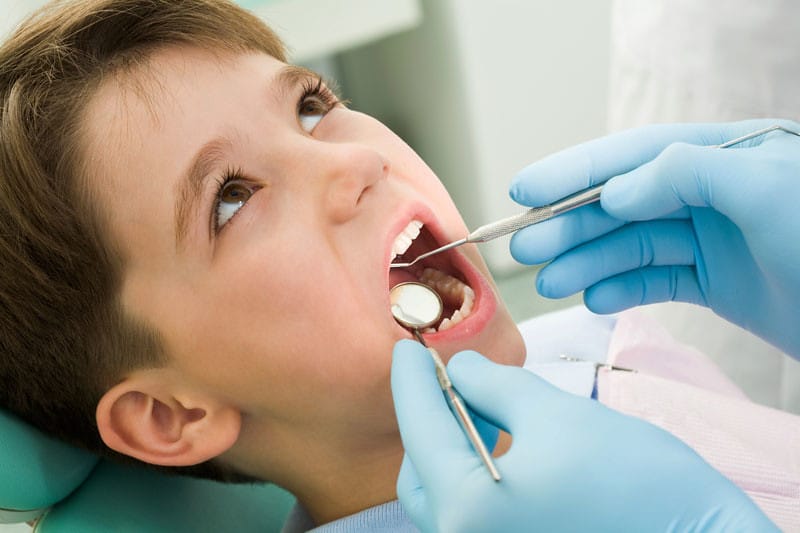
However, why is sedation dentistry for children a separate topic of discussion at all? This is because sedation dosages for children need to be determined very carefully. It is settled according to the child’s age, body weight and other parameters. This post deals elaborately in the various dos and don’ts of pediatric sedation.
How safe is dental sedation for kids?
To begin with, there are different levels of anesthesia (that will be discussed later in this article). Amongst these, if your child’s sedation is general anesthesia, there needs to be an extra amount of caution into it. The reason is that children often have the tendency of falling down to a deeper degree of sedation than the actual intended amount!
It must be regretfully stated that, most unfortunately, unintended sedation levels have dangerously claimed a number of innocent lives in the past decades. The statistics of the last three decades sadly reveals that 44 patients aged between 2 to 5 years died after being exposed to inappropriate levels of sedation. The cases were mostly that, they never recovered from general anesthesia that was administered to them.
Why do children run the risk of getting succumbed to general anesthesia?
Physiologically, the reserve of oxygen in a kid’s body is much less as compared to an older person or even a child above 12. Hence, in case of emergencies, their body is unable to deal with short lapses and succumb to the shortfall. This leads to fatal outcomes.
Tips to keep risk at bay while your child is being sedated
- A hospital visit instead of a dental office (especially in case if it’s your first visit) is of great help. This is because a hospital is always more equipped to deal with emergencies. In a hospital, there’s an alarm that goes out once there is an emergency and there are experts trained personnel to immediately attend to the situation.
- Children with enlarged tonsils are more prone to airway obstruction than adults. This is because kids below the age of 6yrs have a much smaller airway. This can be blocked rather easily. In fact, the size difference (of airways) between a 4-yr old and a 12-yr old is huge. This enhances the risk in the case of smaller children.
- Parents need to extra careful about children who are overweight and obese. The sedative drug that is consumed does not get metabolized readily. It gets stored in the fat cells and hence the recovery time is unnecessarily elongated!
The different types of sedation – which would you, go for?
- Nitrous oxide: Commonly known as laughing gas, NO2 and is the lightest form of any sedative. Children inhale it with a little bit of oxygen, the effect being – staying a little light-headed and relaxed. This keeps them a little less restless and troublesome while sitting in front of the dentist.
- Mild sedation: This level of sedation does keep your child wide awake and conscious. The purpose is to only to make the child just slightly drowsy such that he or she remains calm while in the dental chair. Consciousness is essential in order to administer medications. After the procedure, the child would possibly not even remember things about the dental visit. Dentists can safely give the medications while doing the dental work, as your child remains awake.
- Moderate sedation: The drowsiness, in this case, is a little deeper than the mild sedation. It is usually administered to older children, teenagers and young adults. It is easy to continue with the dental work and other medications when the patient is a little grown-up. Younger and more fearful children tend to nearly lose their consciousness and power of understanding if exposed to moderate sedation. The older ones will still be able to perceive what the dentist says and recover easily too.
- Deep sedation: This is administered by intravenous (IV) means. It makes the child sleep through the procedure. Since the level of consciousness, in this case, is very less, breathing might not take place normally. Therefore, the presence of an anesthesiologist is of utmost importance. He will monitor your child’s heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation (breathing) during the dental procedure and also until he or she wakes up. Your child goes home only once your anesthesiologist permits the kid to do so.
- General anesthesia: As already discussed above, general anesthesia needs the dentist to be extra cautious. Anesthetic experts will have to be monitoring the child, determine the amount of anesthesia that needs to be administered according to the patient’s body weight and other parameters. Post-surgery the anesthetist plays a major role too. Despite all these, it goes without mentioning that anesthesia can be given only in a dental office that is specially equipped or a hospital. At least the office needs to be armed with an ambulance!
Dietary restrictions before and after surgery
Medically, sedation dentistry is equally safe and applicable in case of children as that of adults. Only the dental experts and also the other office staff need to be specially trained to be able to handle kids. The role of parents is to swipe away the dental anxiety from within their children as far as possible and strictly stick to specific diet norms before and after oral surgery. Some of the eating to-dos include:
- No solid food to be given to the child from midnight prior to the day of his/her dental visit.
- Only clear liquids can be taken up to 2 hours before your arrival time at the dental office. However, they must be clear, see-through liquids. No pulps or formula food is allowed. Even milk is not a clear liquid!
The swelling and soreness after any dental procedure would remain for a few days post your return from sedation Dentists at Keller & Fort Worth, TX. Therefore, it is sternly advised that the child gets complete rest until recovery. Joining school or daycare should be deferred until then.




